An 86 year old diabetic man presents to ED with a 1 month history of diarrhoea and fatigue and intermittent upper abdominal pain over the last week. His ECG is as below.
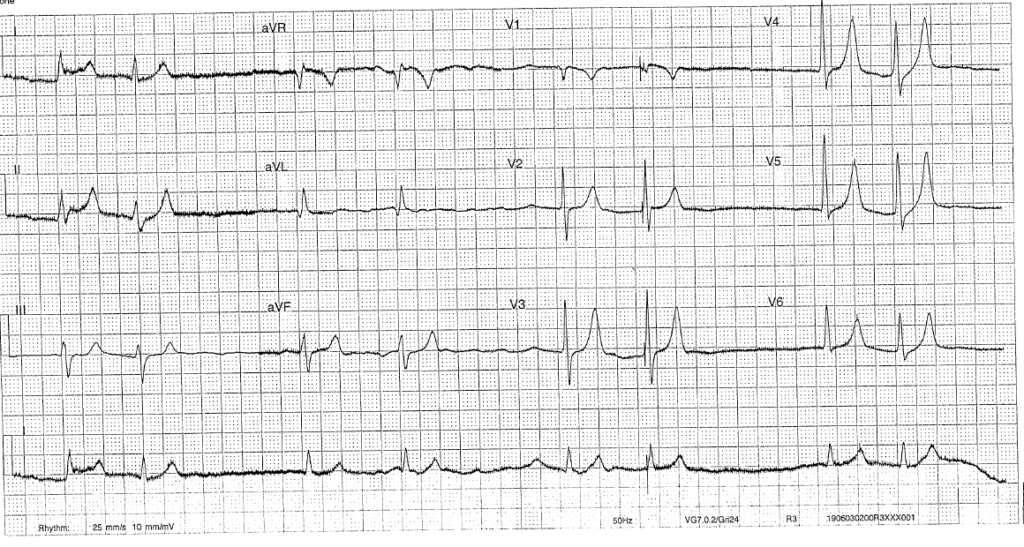
- Rate: 48bpm
- Rhythm: Atrial fibrillation, couplet complexes
- Axis: Normal
- Morphology: Normal
- Intervals: QRS normal
- Other: peaked T waves (II >5mm, V3-5 >10mm)
What investigations would you like to do next?
- BSL 13.4 /Ketones 0.1
- VBG: pH7.20 CO2 44.1 O2 30.5 HCO3 18.8 Hb 90 Na133 K8.1, Lac 1.5, Cr649
- Trop: 29
- Urea 25
- LFTs/Lipase normal
- CXR mild pulmonary oedema
Management:
- K lowering strategy for severe hyperkalaemia (K>6): Insulin/dextrose, Sablutamol, Calcium Gluconate, IV fluids
- HDU admission – renal failure conservatively managed, nephrotoxic drugs including metformin withheld
- Gastroenteritis managed with IV antibiotics, fluids and antiemetics
Summary:
- Diagnosis made of Acute tubular necrosis 2 blastocystis gastroenteritis
- Acute on chronic diabetic renal failure 2 pre-renal AKI (last Cr 265) identified
- Hyperkalaemia 2 AKI
- Tented t waves most easily seen in precordial leads
- See loss of p waves in severe hyperkaelamia (K>8) due to impaired SAN automaticity and AVN conduction.
Further Reading:
- Chan TC, Brady WJ, Harrigan RA, Ornato JP, Rosen P. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. Elsevier Mosby 2005.

 Interpretation:
Interpretation: