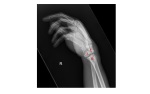
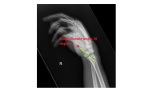
The lateral wrist x-ray shows a peri-lunate dislocation. The capitate, along with the distal metacarpal attachment, has been displaced posteriorly.
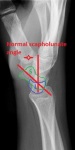
The proximal lunate is in line with the distal radius, but the distal surface of the lunate is tilted forward. This abnormality of the lunate is called the Volar Intercalated Segmental Instability (VISI). This is a type of carpal instability wherein the scapho-lunate angle is under 30° and in this particular case, it is only 10°. A scapho-lunate angle is the angle between the lunate short axis and the scaphoid long axis and normally possesses a value of 30-40°.
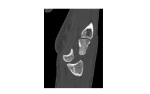
A CT scan done to further characterise the injury showed a greater arc injury, including a trans-scaphoid perilunate dislocation and VISI. The patient underwent surgical correction.
Reference: Grainger and Allison’s Diagnostic Radiology Essentials.