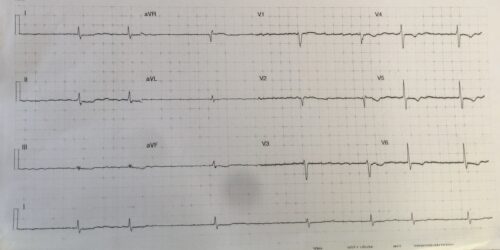
A 79 year old male presents to ED after a syncope. The patient has had diarrhoea and vomiting over the past week. He has a background of hypertension, atrial fibrillation and CCF. Below is the patients ECG:
Describe and Interpret the ECG
Answer:
Rate: ventricular rate 42 beats per minute
Rhythm: Slow atrial fibrillation
Axis: Normal axis
Intervals:
QRS: 100ms
QTc: 391ms (Fridericia) (Difficult to assess due to flattened T waves and biphasic T/U wave in lateral leads)
Additional:
Flattened T waves in limb leads and ST depression II and aVF
Biphasic/Inverted T waves V4 -V6
The above ECG shows slow AF with T wave and ST changes. In the clinical context of diarrhoea and vomiting, and a background of AF and CCF, electrolyte disturbances and digoxin toxicity need to be considered. Low potassium, magnesium and calcium can cause flattened T waves and ST segments.
Digoxin toxicity can cause: bradycardias, increased automaticity with ventricular ectopic, bigeminy, SVT and VT’s, as well as syncope and hypotension.
The diagnosis needs to be considered in any patient on digoxin who presents with syncope, GI complaints, hypotension, brady and tachyarrhythmias or altered GCS. Mortality can be up to 30%.
If the patient is on digoxin, in the case of chronic digoxin toxicity, serum digoxin levels near therapeutic range correlate poorly with severity of intoxication.
References
Murray, L. et al. Toxicology Handbook, second edition. Churchhill Livingstone.