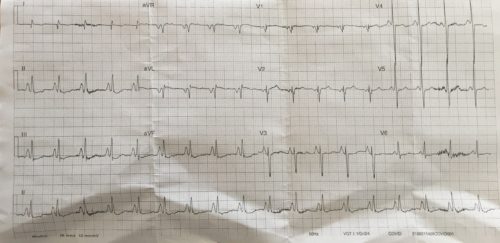
A 60 year old female presents to ED after a heroin OD. The patient has a background of COPD and malnutrition. An ECG is done:
Describe and interpret the ECG
Answer
Rate: 108 beats/min
Rhythm: Sinus tachycardia
Axis: Vertical axis (90 Degrees using the isoelectric method)
Intervals
- PR 100ms
- QRS 90ms
- QTc 456ms (Bazett)
Additional:
Peaked enlarged P waves best seen in the inferior leads >2.5mm in amplitude
Poor R wave progression in chest leads.
Flattening of T waves and ST depression inferiorly and V3 and V4
The above ECG shows typical findings of a patient with COPD. Flattening of the diaphragm leads to the heart being pulled vertically and rotation of the heart occurs with movement of the right ventricle anteriorly and left ventricle posteriorly. This leads to the vertical/right axis deviation and poor R wave progression in the chest leads. Pulmonary pressures increase leading to right atrial and ventricular enlargement. The right atrial enlargement can be seen on this ECG by the prominent P wave amplitude inferiorly and the P wave right axis (inverted P wave in aVL)
The T Wave flattening and ST depression can be due to hypokalaemia from salbutamol use or other electrolyte disorders secondary to the patients underlying malnutrition.
The cause of the shortened PR interval in this case is unknown, the patient might have an underlying accessory pathway or it might be related to underlying cardiomyopathy.
Reference
Chan,T et al ECG in Emergency Medicine, Philadelphia, Elsevier Mosby, 2005